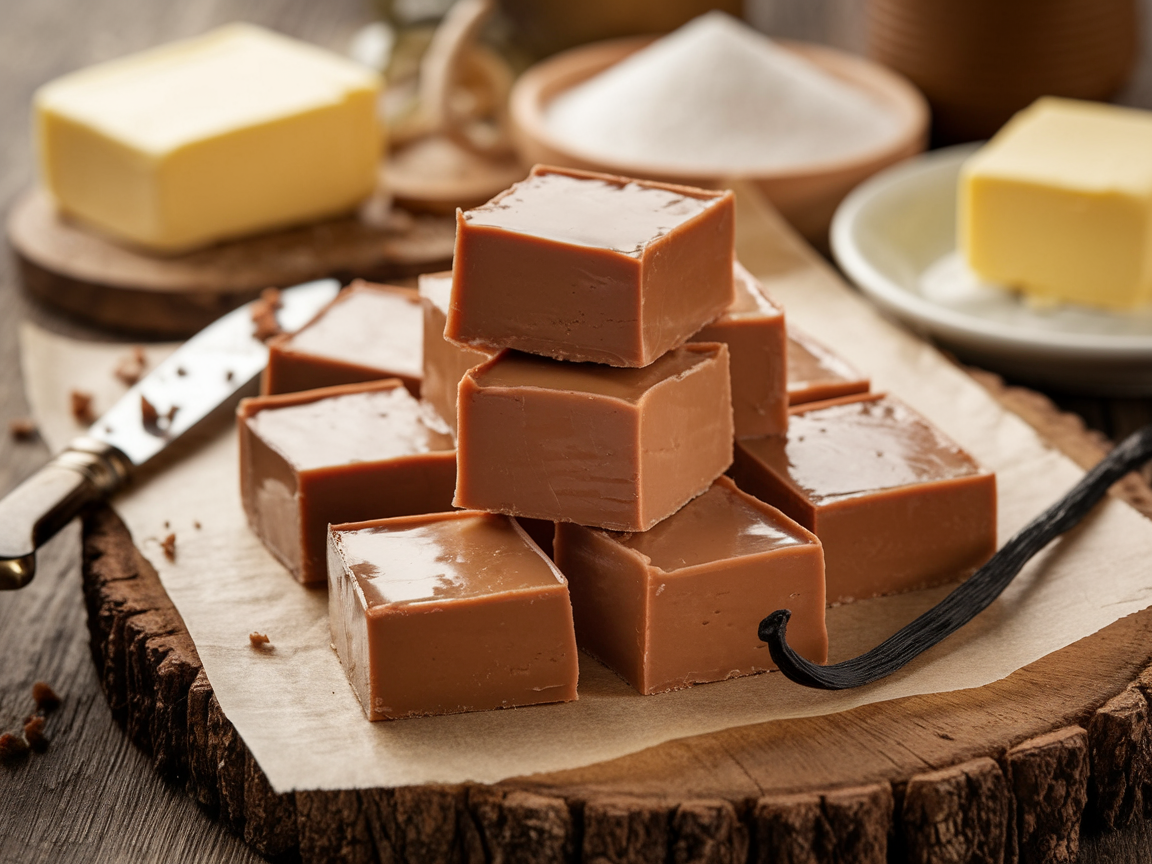
Fudge is a classic confectionery treat cherished for its smooth texture and rich flavor. Traditional fudge, in particular, holds a special place in the world of sweets for its simple ingredients and timeless preparation methods. In this article, we’ll explore what traditional fudge is made of, its variations, and how it compares to modern adaptations.
The Core Ingredients of Traditional Fudge
At its heart, traditional fudge is a straightforward recipe, relying on just a few key ingredients that combine to create a decadent result.
1. Sugar
- Role: Acts as the base and provides structure to the fudge.
- Types Used: Granulated sugar is most common, as it melts and crystallizes well when heated.
2. Dairy Products
- Butter: Adds richness and a creamy texture.
- Milk or Cream: Provides moisture and helps achieve the fudge’s signature softness.
3. Flavor Enhancers
- Vanilla Extract: The classic flavoring for traditional fudge.
- Salt: Balances the sweetness and deepens the flavor profile.
4. Stabilizers
- Corn Syrup or Cream of Tartar: These prevent the sugar from crystallizing too quickly, ensuring a smooth texture.
For more insight into baking fundamentals, check out what does buttermilk do in cakes, which discusses how similar ingredients enhance confectionery textures.
The Science Behind Fudge
Creating the perfect traditional fudge involves precision and understanding the science behind the process.
1. Heating the Mixture
- Sugar, butter, and milk are heated together to the “soft-ball stage” (234°F–240°F).
- A candy thermometer is essential to ensure the right temperature is reached.
2. Cooling and Beating
- After heating, the mixture is cooled without stirring to avoid premature crystallization.
- Beating begins once it cools slightly, introducing air and achieving the desired creamy texture.
Types of Traditional Fudge
While the base recipe is simple, traditional fudge can be adapted with various flavors and textures.
1. Chocolate Fudge
- Made by adding cocoa powder or melted chocolate to the base ingredients.
- Offers a richer, more indulgent taste.
2. Vanilla Fudge
- Focuses on the buttery and sweet vanilla flavor, without the addition of cocoa.
3. Nut and Fruit Variations
- Popular add-ins include walnuts, pecans, or dried fruits like cranberries.
If you’re looking for creative dessert inspiration, visit what is the most delicious dessert in the world to explore global confectionery favorites.
Traditional Fudge vs. Modern Variations
1. Old-Fashioned Fudge
- Relies solely on the core ingredients (sugar, butter, milk) and requires careful monitoring of temperature.
- Known for its pure, rich flavor and creamy consistency.
2. Modern Fudge
- Often includes shortcuts like sweetened condensed milk or marshmallow fluff for ease.
- Faster to make but lacks the depth of flavor found in traditional recipes.
Tips for Making Perfect Traditional Fudge
- Use a Candy Thermometer: Precision in temperature is key to achieving the right texture.
- Avoid Stirring While Boiling: Stirring can cause unwanted crystallization, leading to grainy fudge.
- Let It Cool Before Beating: Patience ensures a smoother texture.
Popular Uses for Traditional Fudge
Traditional fudge isn’t just a standalone treat—it has multiple uses:
1. Gift Giving
- Homemade fudge is a thoughtful and delightful present for holidays and special occasions.
2. Desserts
- Crumble fudge into brownies or use it as an ice cream topping.
3. Tea-Time Treat
- Pair fudge with coffee or tea for a luxurious snack.
For more practical dessert ideas, consider what foods have 5 ingredients or less.
FAQs About Traditional Fudge
1. What makes traditional fudge smooth?
The key is proper temperature control and consistent beating after cooling to create fine sugar crystals.
2. Can I make fudge without a candy thermometer?
While possible, using a thermometer ensures accuracy and consistency.
3. Why does fudge sometimes turn out grainy?
Grainy texture occurs when sugar crystallizes too quickly, often due to stirring during boiling.
4. Can traditional fudge be made dairy-free?
Yes, substitute plant-based butter and coconut or almond milk for the dairy ingredients.
5. How should I store traditional fudge?
Store in an airtight container at room temperature for up to two weeks, or freeze for longer storage.
Internal Linking Opportunities
- Explore what does buttermilk do in cakes for tips on enhancing baked goods.
- Check out what is the most delicious dessert in the world for dessert inspiration.
- Learn about what makes German chocolate special to expand your confectionery knowledge.
Conclusion
Traditional fudge is a timeless treat that combines simplicity with indulgence. Made from basic ingredients like sugar, butter, and milk, it showcases the art of precise cooking and careful preparation. Whether you enjoy it plain or with added flavors and textures, fudge is a versatile dessert that brings joy to any occasion.
Now that you know what traditional fudge is made of and how it’s prepared, why not try making it at home? Experiment with flavors, share it with loved ones, and savor the magic of this classic confection!